What is a Cascade Refrigeration System? All You Need To Know
The cascade refrigeration system is a freezing system that uses two kinds of refrigerants having different boiling points, which run through their own independent freezing cycle and are joined by a heat exchanger. The schematic view and the P-h diagram of this system are shown below.
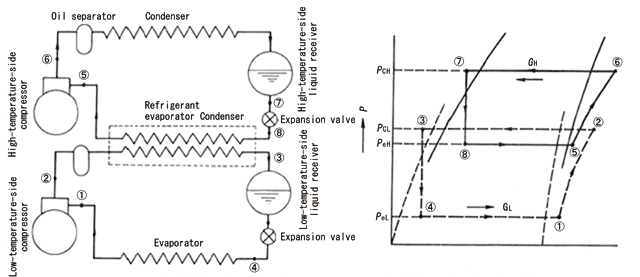
This system is employed to obtain temperatures of -40 to -80°C or ultra-low temperatures lower than them.
At such ultra-low temperatures, a common single-refrigerant two-stage compression system limits the low-temperature characteristics of the refrigerant to a considerably poor level, making the system significantly inefficient. The efficiency is improved by combining two kinds of refrigerants having different temperature characteristics.

This system is employed to obtain temperatures of -40 to -80°C or ultra-low temperatures lower than them.
At such ultra-low temperatures, a common single-refrigerant two-stage compression system limits the low-temperature characteristics of the refrigerant to a considerably poor level, making the system significantly inefficient. The efficiency is improved by combining two kinds of refrigerants having different temperature characteristics.
Here are the key points to understand about cascade refrigeration systems:
Basic Concept
1. *Two or More Stages*: The system is divided into stages, each operating at different temperature levels and using different refrigerants optimized for those temperature ranges.
2. *Heat Exchange*: The evaporator of one stage (low-temperature cycle) acts as the condenser for the next stage (high-temperature cycle).
Components
1. *Compressors*: Each stage has its own compressor, suited for the specific refrigerant used.
2. *Condensers and Evaporators*: Each stage has condensers and evaporators. The condenser of the lower stage cools the evaporator of the higher stage.
3. *Heat Exchanger*: Acts as an interface between stages, transferring heat from the lower stage to the higher stage.
1. *Two or More Stages*: The system is divided into stages, each operating at different temperature levels and using different refrigerants optimized for those temperature ranges.
2. *Heat Exchange*: The evaporator of one stage (low-temperature cycle) acts as the condenser for the next stage (high-temperature cycle).
Components
1. *Compressors*: Each stage has its own compressor, suited for the specific refrigerant used.
2. *Condensers and Evaporators*: Each stage has condensers and evaporators. The condenser of the lower stage cools the evaporator of the higher stage.
3. *Heat Exchanger*: Acts as an interface between stages, transferring heat from the lower stage to the higher stage.
Operation
1. *High-Temperature Stage*: The first stage operates at a higher temperature using a refrigerant suitable for higher temperatures. It cools the condenser of the lower-temperature stage.
2. *Low-Temperature Stage*: The second stage operates at a much lower temperature using a different refrigerant suitable for low temperatures. It provides the desired low cooling temperature.
1. *High-Temperature Stage*: The first stage operates at a higher temperature using a refrigerant suitable for higher temperatures. It cools the condenser of the lower-temperature stage.
2. *Low-Temperature Stage*: The second stage operates at a much lower temperature using a different refrigerant suitable for low temperatures. It provides the desired low cooling temperature.
Advantages
1.*Efficient Low-Temperature Cooling*: Achieves very low temperatures that single-stage systems cannot reach efficiently.
2. *Optimized Refrigerant Use*: Different refrigerants can be used for different stages, each optimized for specific temperature ranges.
Applications
1. *Cryogenics*: Used in industries requiring very low temperatures, such as cryogenic research and medical applications (e.g., storing biological samples).
2. *Chemical Industry*: Used for processes requiring very low temperatures, such as liquefaction of gases.
3. *Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers*: Common in laboratories and medical facilities.
1.*Efficient Low-Temperature Cooling*: Achieves very low temperatures that single-stage systems cannot reach efficiently.
2. *Optimized Refrigerant Use*: Different refrigerants can be used for different stages, each optimized for specific temperature ranges.
Applications
1. *Cryogenics*: Used in industries requiring very low temperatures, such as cryogenic research and medical applications (e.g., storing biological samples).
2. *Chemical Industry*: Used for processes requiring very low temperatures, such as liquefaction of gases.
3. *Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers*: Common in laboratories and medical facilities.
Example Configuration
*First Stage: Uses a refrigerant like R-404A, operating at a moderate temperature range.
*Second Stage: Uses a refrigerant like R-23, operating at a much lower temperature range.
*Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the first stage to the second stage, allowing the second stage to achieve very low temperatures.
Challenges
1. *Complexity*: More complex than single-stage systems, requiring precise control and maintenance.
2. *Cost*: Higher initial cost due to multiple stages and components.
Cascade refrigeration systems are essential for applications requiring extreme cooling, providing efficiency and flexibility by leveraging the advantages of different refrigerants across multiple stages.
1. *Complexity*: More complex than single-stage systems, requiring precise control and maintenance.
2. *Cost*: Higher initial cost due to multiple stages and components.
Cascade refrigeration systems are essential for applications requiring extreme cooling, providing efficiency and flexibility by leveraging the advantages of different refrigerants across multiple stages.







No comments:
Post a Comment